
Subscribe to continue reading
Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.

Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.
Unlock the secrets to enhanced productivity and seamless project management.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, mastering the art of productivity is not just an option, but a necessity. The dynamic duo of Microsoft Planner and Power Automate are our allies in the realm of project and task management. Imagine a world where our projects flow seamlessly, where every task aligns perfectly with your goals, and efficiency is not just a buzzword but a daily reality. This is all achievable with the integrations of Microsoft Planner and Power Automate in your corner.
Microsoft Planner, is our go-to task management tool, that allows us and our teams to effortlessly create, assign, and monitor tasks. It provides a central hub where tasks aren’t just written down but are actively managed and collaborated on. Its strength lies in its visual organization of tasks, with dashboard and progress indicators providing an bird’s-eye view of our project, making organization and prioritization a breeze. It is about managing the chaos of to-dos into an organized methodology of productivity, with each task moving smoothly from To Do to Done.
On the other side of this partnership we have Power Automate, the powerhouse of process automation. It bridges the gap between our various applications and services, automating the mundane so we can focus on what is important. Power Automate is our behind the scenes tool for productivity, connecting our favorite apps and automating workflows whether that’s collecting data, managing notifications, sending approvals, and so much more all without us lifting a finger, after the initial setup of course.
Together, these tools don’t just manage tasks; they redefine the way we approach project management. They promise a future where deadlines are met with ease, collaboration is effortless, and productivity peaks are the norm.
Ready to transform your workday and elevate your productivity? Let Microsoft Planner and Power Automate streamline your task management.
Here’s an overview of what is explored within this post. Start with an overview of Power Automate triggers and actions specific to Microsoft Planner or jump right to some example workflows.
Exploring Planner triggers in Power Automate reveals a world of automation that streamlines task management and enhances productivity. Let’s dive into three key triggers and their functionalities.
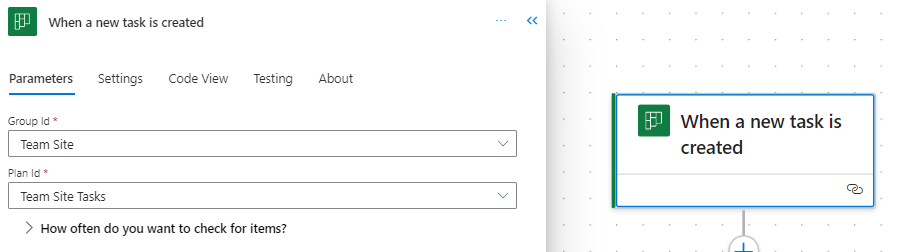
This trigger jumps into action as soon as a new task is created in Planner. It requires the Group Id and Plan Id to target the specific Planner board. This trigger can set a series of automated actions into motion, such as sending notifications to relevant team members, logging the task in an Excel reporting workbook, or triggering parallel tasks in a related project.
This trigger personalizes your task management experience. It activates when a task in Planner is assigned to you. This trigger can automate personal notifications, update your calendar with the new tasks, or prepare necessary documents or templates associated with the task. Simply select this Planner trigger and it is all set, there is no additional information required by the trigger. It’s an excellent way to stay on top of personal responsibilities and manage your workload efficiently.

The completion of a task in Planner can signal the start of various subsequent actions, hinging on the completion status of a task in a specified plan. The required inputs are the Group Id and the Plan Id to identify the target Planner board. This trigger is instrumental in automating post-task processes like updating project status reports, notifying team members or stakeholders of the task completion, or archiving task details for accountability and future reference.

By leveraging these Planner triggers in Power Automate, we can not only automate but also streamline our workflows. Each trigger offers a unique avenue to enhance productivity and ensures that our focus remains on strategic and high-value tasks.
Navigating the complexities of project management requires tools that offer both flexibility and control. The integration of Microsoft Planner actions within Power Automate provides a robust solution for managing tasks efficiently. By leveraging Planner actions in Power Automate, we can automate and refine our task management processes. Let’s dive into some of the different Planner actions.
Task assignment is a critical aspect of project management. These actions in Power Automate facilitate flexible and dynamic assignment and reassignment of team members to tasks in Planner, adapting to the ever-changing project landscape.
Add assignees to a task
This action allows us to assign team members to specific tasks, with inputs including the task ID and the user ID(s) of the assignee(s). It’s particularly useful for quickly adapting to changes in project scope or team availability, ensuring that tasks are always in the right hands.

Remove assignees from a task
Inputs for this action are the task ID and the user ID(s) of the assignee(s) to be removed. It’s essential for reorganizing task assignments when priorities shift or when team members need to be reallocated to different tasks, maintaining optimal efficiency.
The lifecycle of a task within any project involves its creation and eventual completion or removal. These actions in Power Automate streamline these essential stages, ensuring seamless task management within Planner.
Create a task
Every project begins with a single step, or in the case of our Planner board, a single task. To create a task we must provide the essentials, including Group Id, Plan Id, and Title. This action is invaluable for initiating tasks in response to various Power Automate triggers, such as email requests or meeting outcomes, ensuring timely task setup.

When using the new Power Automate designer (pictured above), be sure to provide all optional details of the task by exploring the Advanced parameters dropdown. Under the advanced parameters we will find task details to set in order to create a task specific to what our project requires. We can set the newly created task’s Bucket Id, Start Date Time, Due Date Time, Assigned User Id, as well as applying any tags needed to create a detailed and well defined task. When using the classic designer we will see all these options listed within the action block.
Delete a task
Keeping our Planner task list updated and relevant is equally important to successful project lifecycle management. Removing completed, outdated, or irrelevant tasks can help us maintain clarity and focus on the overall project plan. This action just requires us to provide the Task Id of the task we want deleted from our Planner board.
Accessing and updating task information are key aspects of maintaining project momentum. These actions provide the means to efficiently manage task within Planner.
Get a task
Understanding each task’s status is crucial for effective management, and the Get a task action offers a window into the life of any task in our Planner board. By providing the Task Id, this action fetches the task returning information about the specific task. It is vital for our workflows that require current information about a task’s status, priority, assignees, or other details before proceeding to subsequent steps. This insight is invaluable for keeping a pulse on our projects progress.

Update a task
This action, requires the Task Id and the task properties to be updated, allowing for real-time modifications of task properties. It is key for adapting tasks to new deadlines, changing assignees, or updating a task’s progress. Using this action we can ensure that our Planner board always reflects the most current state of our tasks providing a current overview of the overall project status.

Detailed task management is often necessary for complex projects. These actions cater to this need by providing and updating in-depth information about tasks in Planner.
Get task details
Each task in a project has its own story, filled with specific details and nuances. This action offers a comprehensive view of a task, including its description, checklist items, and more. It is an essential action for workflows that require a deep understanding of task specifics for reporting, analysis, or decision making.

Update task details
With inputs for detailed aspects of our tasks, such as its descriptions and checklist items, this action allows for precise and thorough updates to our task information. It is particularly useful for keeping tasks fully aligned with project developments and team discussions.

Effective task categorization is vital for clear project visualization and management. The List buckets action in Power Automate is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of task categories or buckets within our Planner board. We provide this action the Group Id and Plan Id and it returns a list of all the buckets within the specified plan, including details like bucket Id, name, and an order hint.
This information can aid in our subsequent actions, such as creating a new task within a specific bucket on our Planner board.

Keeping a tab on all tasks within a project is essential for effective project tracking, reporting, and management. The List tasks action in Power Automate offers a detailed view of tasks within a specific planner board.
We need to provide this action the Group Id and Plan Id, and it provides a detailed list of all tasks. The details provided for each task include the title, start date, due date, status, priority, how many active checklist items the task has, categories applied to the task, who created the task, and who the task is assigned to. This functionality is invaluable for teams to gain insights into task distribution, progress, and pending actions, ensuring that no task is overlooked and that project milestones are met.

Before diving into some more advanced examples and integrations, it is essential to understand how Planner and Power Automate can simplify everyday task management through some basic workflows. These workflows will provide a glimpse into the potential of combining these two powerful tools.
This workflow automates the process of summarizing completed tasks in Planner, sending a weekly email to project managers so they can keep their finger on the pulse of project progress.
The flow has a reoccurrence trigger which is set to run the workflow on a weekly basis. The workflow then starts by gathering all the tasks from the planner board using the List tasks action. This action provides two helpful task properties that we can use to pinpoint the task that have been completed in the last week.
The first is percentComplete, we add a filter data operation action to our workflow and filter to only tasks that have a percentComplete equal to 100 (i.e. are marked completed). We set the From input to the value output of the List task action and define our Filter Query.

The second property we can use from List tasks is the completedDateTime, we can use this to further filter our completed task to just those completed within the last week. Here we use the body of our Filter array: Completed tasks action and use an expression to calculated the difference between when the task was completed and when the flow is ran, in days.

The expression used in the filter query is:
int(split(dateDifference(startOfDay(getPastTime(1, 'Week')), item()?['completedDateTime']), '.')[0])
This expression starts by getting the start of the day 1 week ago using getPastTime and startOfDay. Then we calculate the difference using dateDifference. The date difference function will return a string value in the form of 7.00:00:00.0000000, representing Days.Hours:Minutes:Seconds. For our purposes we are only interested in the number of days, specifically whether the value is positive or negative, that is was it completed before or after the date 1 week ago. To extract just the days as an integer we first use split to split the string based on periods, and then we use the first item in the resulting array ([0]), and pass this to the int function, to get a final integer value.
We then use the Create HTML table action to create a summary table of the Planner tasks that were completed in the past week.

Then we can send out an email to those that require the weekly summary of completed tasks, using the output of the Create HTML table: Create summary table action.

Here is an overview of the entire Power Automate workflow that automates our process of summarizing our Planner tasks that have been completed in the past week.

This automated summary is invaluable for keeping track of progress and upcoming responsibilities, ensuring that our team is always aligned and informed about the week’s achievements and ready to plan for what is next.
This workflow is tailored to enhance team awareness and acknowledgement of completed high-priority tasks. It automatically sends a Teams notification when a high-priority task in Planner is marked as completed.
The workflow triggers when a Planner task on the specified board is marked complete. The workflow then examines the priority property of the task to determine if a notification should be sent. For the workflow a high-priority task is categorized as a task marked as Important or Urgent in Planner.

The workflow uses a condition flow control to evaluate each task’s priority property. An important note here is that, although in Planner the priorities are shown as Low, Medium, Important, and Urgent, the property values associated with these values are stored in the task property as 9, 5, 3, 1, respectively. So the condition used evaluates to true if the priority value is less than or equal to 3, that is the task is Important or Urgent.
When the condition is true, the workflow gathers more details about the task and then sends a notification to keep the team informed about these critical tasks.

Let’s break down the three actions used to compose and send the Teams notification. First, we use the List buckets action to provide a list of all the buckets contained within our Planner board. We need this to get the user friendly bucket name, because the task item only provides us the bucket id.
Then we can use use the Filter data operation to filter the list of all the buckets to the specific bucket the complete task resides in.

Here, value is the output of our List bucket action, id is the current bucket list item, and bucketId is the id of the current task item of the For each: Completed task loop. We can then use the dynamic content from the output of this action to provide a bit more detail to our Teams notification.
Now we can piece together helpful information and notify our team when high-priority tasks are completed using the Teams Post a message in a chat or channel action, shown above. Providing our team details like the task name, the bucket name, and a link to the Planner board.
These basic yet impactful workflows illustrate the seamless integration of Planner with Power Automate, setting the stage for more advanced and interconnected workflows. They highlight how simple automations can significantly enhance productivity and team communication.
The integration of Microsoft Planner with other services through Power Automate unlocks new dimensions in project management, offering innovative ways to manage tasks and enhance collaboration.
A standout application of this integration is the reporting of Planner tasks in Excel. By establishing a flow in Power Automate, task updates from Planner can be seamlessly merged to an Excel workbook. This setup is invaluable for generating detailed reports, tracking project progress, and providing more in-depth insights.
For an in-depth walkthrough of a workflow, leveraging this integration check out this post that covers the specifics of setting up and utilizing this integration.

Transforming Project Tracking: How to Merge Planner with Excel Using Power Automate
Explore the Detailed Workflow for Seamless Task Management and Enhanced Reporting Capabilities.
Combining Planner with GitHub through Power Automate creates a streamlined process for managing software development tasks. A key workflow in this integration is the generation of Planner tasks in response to new GitHub issues assigned to you. When an issue is reported in GitHub, a corresponding task is automatically created in Planner, complete with essential details from the GitHub issue. This integration ensures prompt attention to issues and their incorporation into the broader project management plan.
Check back, for a follow up post focus specifically on providing a detailed guide on implementing this workflow.
These advanced workflows exemplify the power and flexibility of integrating Planner with other services. By automating interactions across different platforms, teams can achieve greater efficiency and synergy in their project management practices.
Finishing our exploration of Microsoft Planner and Power Automate, it’s evident that these tools are more than mere facilitators of task management and workflow automation. They embody a transformative approach to project management, blending efficiency, collaboration, and innovation in a unique and powerful way.
The synergy between Planner and Power Automate opens up a realm of possibilities, enabling teams and individuals to streamline their workflows, integrate with a variety of services, and automate processes in ways that were previously unimaginable. From basic task management to complex, cross-platform integrations with services like Excel and GitHub, these tools offer a comprehensive solution to the challenges of modern project management.
The journey through the functionalities of Planner and Power Automate is a testament to the ever-evolving landscape of digital tools and their impact on our work lives. As these tools continue to evolve, they offer fresh opportunities for enhancing productivity, fostering team collaboration, and driving innovative project management strategies.
Experiment with these tools and explore the myriad of features they have to offer, and discover new ways to optimize your workflows. The combination of Planner and Power Automate isn’t just a method for managing tasks; it’s a pathway to redefining project management in the digital age, empowering teams to achieve greater success and efficiency.
Thank you for reading! Stay curious, and until next time, happy learning.
And, remember, as Albert Einstein once said, “Anyone who has never made a mistake has never tried anything new.” So, don’t be afraid of making mistakes, practice makes perfect. Continuously experiment, explore, and challenge yourself with real-world scenarios.
If this sparked your curiosity, keep that spark alive and check back frequently. Better yet, be sure not to miss a post by subscribing! With each new post comes an opportunity to learn something new.
Elevate Your Power BI Reports with Context-Aware Insights
Welcome, to another journey through the world of DAX, in this post we will be shining the spotlight on the ISINSCOPE function. If you have been exploring DAX and Power BI you may have encountered this function and wondered its purpose. Well, wonder no more! We are here to unravel the mysteries and dive into some practical example showing just how invaluable this function can be in our data analysis endeavors.
If you are unfamiliar DAX is the key that helps us unlock meaningful insights. It is the tool that lets us create custom calculations and serve up exactly what we need. Now, lets focus on ISINSCOPE, it is a function that might not always steal the show but plays a pivotal role, particularly when we are dealing with hierarchies and intricate drilldowns in our reports. It provides us the access to understand at which level of hierarchy our data is hanging out, ensuring our calculations are always in tune with the context.
For those of you eager to start experimenting there is a Power BI report pre-loaded with the sample data used in this post ready for you. So don’t just read, follow along and get hands-on with DAX in Power BI. Get a copy of the sample data file (power-bi-sample-data.pbix) here:

GitHub – Power BI DAX Function Series: Mastering Data Analysis
This dynamic repository is the perfect place to enhance your learning journey.
Let’s dive in and get hand on with the ISINSCOPE function. Think of this function as our data GPS, it helps us figure out where we are in the grand scheme of our data hierarchies.
So, what exactly is ISINSCOPE? In plain terms, it is a DAX function used to determine if a column is currently being used in a specific level of a hierarchy or, put another way, if we are grouping by the column we specify. The function returns true when the specified column is the level being used in a hierarchy of levels. The syntax is straightforward:
ISINSCOPE(column_name)
The column_name argument is the name of an existing column. Just add a column that we are curious about, and ISINSCOPE will return true or false depending on whether that column is in the current scope.
Let’s use a simple matrix containing our Region, Product Category, and Product Code to set up a hierarchy and see ISINSCOPE in action with the following formula.
ISINSCOPE =
SWITCH(
TRUE(),
ISINSCOPE(Products[Product Code]), "Product Code",
ISINSCOPE(Products[Product]), "Product",
ISINSCOPE(Regions[Region]), "Region"
)
This formula uses ISINSCOPE in combination with SWITCH to determine the current context, and if true returns a text label indicating what level is in context.

But why is this important? Well, when we are dealing with data, especially in a report or a dashboard, we want our calculations to be context-aware. We want them to adapt based on the level of data we are looking at. ISINSCOPE allows us to create measures and calculated columns that behave differently at different levels of granularity. This helps provide accurate and meaningful insights.
Now that we have got a handle on what ISINSCOPE is, let’s dive a bit deeper and see how it works. At the heart of it ISINSCOPE is all about context, specifically, row context and filter context.
For an in depth look into Row Context and Filter Context check out the posts below that provide all the details.

Power BI Row Context: Understanding the Power of Context in Calculations
Row Context — What it is, When is it available, and its Implications

Power BI Filter Context: Unraveling the Impact of Filters on Calculations
Filter Context – How to create it and its impact on measures
For our report we are interested in analyzing the last sales date of our products, and want this information in a matrix similar to the example above. We can easily create a Last Sales Date measure using the following formula and add it to our matrix visual.
Last Sales Date = MAX(Sales[SalesDate])

This provides a good start, but not quite what we are looking for. For our analysis the last sales date at the Region level is too broad and not of interest, while the sales date of Product Code is too granular and clutters the visual. So, how do we display the last sales date just at the Product Category (e.g. Laptop) level? Enter ISINSCOPE.
Let’s update our Last Sales Date measure so that it will only display the date on the product category level. Here is the formula.
Product Last Sales Date =
SWITCH(
TRUE(),
ISINSCOPE(Products[Product Code]), BLANK(),
ISINSCOPE(Products[Product]), FORMAT(MAX(Sales[SalesDate]),"MM/dd/yyyy"),
ISINSCOPE(Regions[Region]), BLANK()
)

We use SWITCH in tandem with ISINSCOPE to determine the context, and if Product is in context the measure returns the last sales date for that product category. However, at the Region and Product Code levels the measure will return a blank value.
The use of ISINSCOPE helps enhance the matrix visual preventing it from getting over crowded with information and ensuring that the information displayed is relevant. It acts as a smart filter, showing or hiding data based on where we are in a hierarchy, making our reports more intuitive and user-friendly.
When we are working with data, understanding the relationship between parts and the whole is crucial. This is where hierarchies and drilldowns come into play, and ISINSCOPE is the function that helps us make sense of it all.
Hierarchies allow us to organize our data in a way that reflects real-world relationships, like breaking down sales by region, then product category, then specific products. Drilldowns let us start with a broad view and then zoom in on the details. But how do we keep our calculations accurate at each level? You guessed it, ISINSCOPE.
Let’s look at a DAX measure that leverages ISINSCOPE to calculate the percentage of sales each child represents of the parent in our hierarchy.
Percentage of Parent =
VAR AllSales =
CALCULATE(Sales[Total Sales], ALLSELECTED())
VAR RegionSales =
CALCULATE([Total Sales], ALLSELECTED(), VALUES(Regions[Region]))
VAR RegionCategorySales =
CALCULATE([Total Sales], ALLSELECTED(), VALUES(Regions[Region]), VALUES(Products[Product]))
VAR CurrentSales = [Total Sales]
RETURN
SWITCH(TRUE(),
ISINSCOPE(Products[Product Code]), DIVIDE(CurrentSales, RegionCategorySales),
ISINSCOPE(Products[Product]), DIVIDE(CurrentSales, RegionSales),
ISINSCOPE(Regions[Region]), DIVIDE(CurrentSales, AllSales)
)
The Percentage of Parent measure uses ISINSCOPE to determine the current level of detail we are working with. If we are viewing our sales by region the measure calculates the sales for the region as a percentage of all sales.

But the true power of ISINSCOPE begins to reveal itself as we drilldown into our sales data. If we drilldown into each region to show the product categories we see that the measure will calculate the sales for each product category as a percentage of sales for that region.

And then again, if we drilldown into each product category we can see the measure will calculate the the sales of each product code as a percentage of sales for that product category within the region.

By incorporating this measure into our report, we help ensure that as we drilldown into our data the percentages are always calculated relative to the appropriate parent in our hierarchy. This allows us to provide accurate measures that provide the appropriate context, making our reports more intuitive and insightful.
ISINSCOPE is the key element to maintaining the integrity of our hierarchical calculations. It ensures that as we navigate through different levels of our data our calculations remain relevant and precise, providing a clear understanding of how each part contributes to the whole.
When it comes to DAX and ISINSCOPE a few best practices can ensure that our reports are accurate, performant, and user-friendly. Here are just a few things that can help us make the most out of ISINSCOPE:
ISINSCOPE, make sure to have a solid understanding of row and filter context. Knowing which context we are working with will help us use ISINSCOPE effectively.ISINSCOPE behaves with our data. Complex measures can be built up gradually as we become more comfortable with the function.ISINSCOPE, test them at every level, this helps ensure that our measures work correctly no matter how the users interact with the report.ISINSCOPE is often used in combination with other DAX functions. Learning how it interacts with functions like SWITCH, CALCULATE, FILTER, and ALLSELECTED will provide us more control over our data.Throughout our exploration of the ISINSCOPE function we have uncovered its pivotal role in managing data hierarchies and drilldowns providing for accurate and context-sensitive reporting. Its ability to discern the level of detail we are working with allows for dynamic measures and visuals that adapt to user interactions, making our reports not just informative but interactive and intuitive.
With practice, ISINSCOPE will become a natural part of your DAX toolkit, enabling you to create sophisticated reports that meet the complex needs of any data analysis challenge you might face.
For those looking to continue their journey into DAX and its capabilities there is a wealth of resources available, and a good place to start is the DAX Reference documentation.

Excel Online (Business) – Actions
Learn more about: Power Automate Excel Online (Business) Actions
I have also written about other DAX functions including Date and Time Functions, Text Functions, an entire post focused on the CALCULATE function and an ultimate guide providing a overview of all the DAX function groups.

Temporal Triumphs with DAX Date and Time Functions
Explore the ebb and flow of the temporal dimension of your data with DAX’s suite of Date and Time Functions.

Mastering DAX Text Expressions: Making Sense of Your Data One String at a Time
Stringing Along with DAX: Dive Deep into Text Expressions

Unlocking the Secrets of CALCULATE: A Deep Dive into Advanced Data Analysis in Power BI
Demystifying CALCULATE: An exploration of advanced data manipulation.

The DAX Function Universe: A Guide to Navigating the Data Analysis Tool box
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Data with DAX: From Basic Aggregations to Advanced Time Intelligence
Thank you for reading! Stay curious, and until next time, happy learning.
And, remember, as Albert Einstein once said, “Anyone who has never made a mistake has never tried anything new.” So, don’t be afraid of making mistakes, practice makes perfect. Continuously experiment and explore new DAX functions, and challenge yourself with real-world data scenarios.
If this sparked your curiosity, keep that spark alive and check back frequently. Better yet, be sure not to miss a post by subscribing! With each new post comes an opportunity to learn something new.